As map labeling southwest asia countries takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. The content that follows provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, delving into the geographic, historical, cultural, economic, and political aspects that shape this dynamic region.
From the intricate labeling of individual countries to the identification of key geographic features, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for students, researchers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of Southwest Asia.
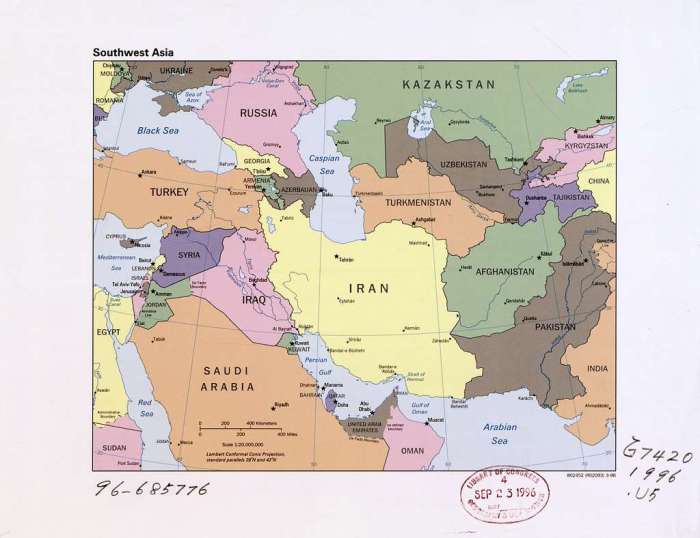
Southwest Asia Country Map
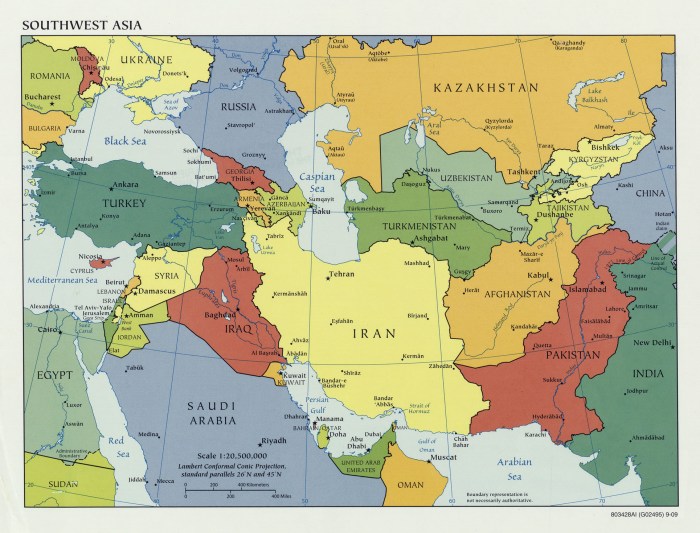
Southwest Asia, also known as the Middle East, is a region of the world located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. It is a diverse region with a rich history and culture, and is home to some of the world’s most important oil and gas reserves.
The following map shows the countries of Southwest Asia, labeled with their corresponding ISO codes:
| Country | ISO Code | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | AFG | Green |
| Bahrain | BHR | Blue |
| Cyprus | CYP | Yellow |
| Egypt | EGY | Red |
| Iran | IRN | Orange |
| Iraq | IRQ | Purple |
| Israel | ISR | Pink |
| Jordan | JOR | Brown |
| Kuwait | KWT | Gray |
| Lebanon | LBN | Black |
| Oman | OMN | White |
| Palestine | PSE | Light Green |
| Qatar | QAT | Light Blue |
| Saudi Arabia | SAU | Light Yellow |
| Syria | SYR | Light Red |
| Turkey | TUR | Light Orange |
| United Arab Emirates | ARE | Light Purple |
| Yemen | YEM | Light Pink |
The map is color-coded for easy identification of each country.
Geographic Features of Southwest Asia
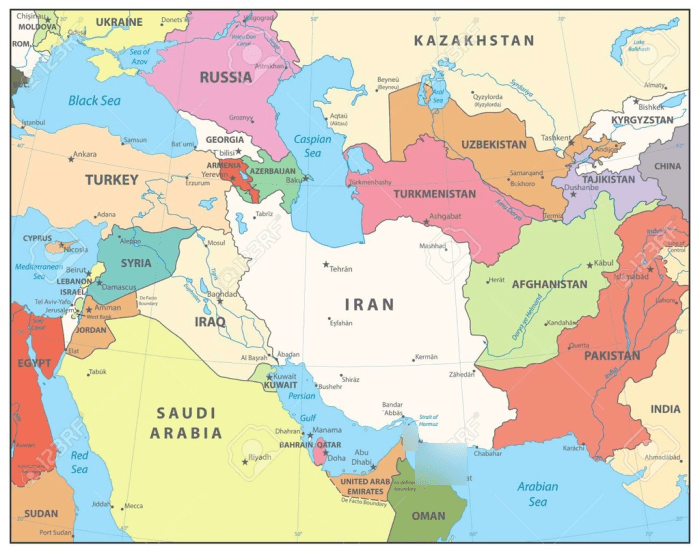
Southwest Asia is a diverse region with a wide range of geographic features. These features have played a significant role in shaping the history and culture of the region.
Major Geographic Features
- Arabian Peninsula:The Arabian Peninsula is a large peninsula located in the southwestern part of Asia. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west, the Arabian Sea to the south, the Persian Gulf to the east, and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast.
The Arabian Peninsula is home to a number of countries, including Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait.
- Persian Gulf:The Persian Gulf is a marginal sea of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula. It is a vital waterway for the global oil trade. The Persian Gulf is also home to a number of important ports, including Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Bandar Abbas.
- Caspian Sea:The Caspian Sea is a large inland sea located between Iran, Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Azerbaijan. It is the largest inland sea in the world. The Caspian Sea is home to a number of important fisheries, and its waters are also rich in oil and gas.
Comparison of Geographic Regions
The following table compares the areas and populations of the different geographic regions within Southwest Asia:
| Region | Area (km²) | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Arabian Peninsula | 3,250,000 | 85,000,000 |
| Persian Gulf | 239,000 | 30,000,000 |
| Caspian Sea | 371,000 | 15,000,000 |
Historical and Cultural Context of Southwest Asia
Southwest Asia, a region of significant historical and cultural importance, has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. It is the birthplace of some of the world’s earliest civilizations and empires, and its rich cultural heritage continues to shape the region today.
The region has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the Akkadian Empire, the Babylonian Empire, the Persian Empire, and the Ottoman Empire. Each of these empires left a lasting impact on the region, contributing to its cultural, political, and economic development.
Ancient Civilizations
- Mesopotamia: The region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, considered the cradle of civilization, was home to the Sumerian, Akkadian, and Babylonian civilizations.
- Ancient Egypt: Although not geographically part of Southwest Asia, Ancient Egypt had a profound influence on the region, particularly through its cultural and economic exchanges.
- Indus Valley Civilization: Flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, this civilization is known for its advanced urban planning and sophisticated water management systems.
Timeline of Key Historical Events
- c. 3500 BCE: Rise of the Sumerian civilization in Mesopotamia.
- c. 2300 BCE: Establishment of the Akkadian Empire by Sargon of Akkad.
- c. 1792 BCE: Hammurabi, king of Babylon, codifies the famous Code of Hammurabi.
- c. 539 BCE: Cyrus the Great conquers Babylon and establishes the Persian Empire.
- c. 331 BCE: Alexander the Great conquers the Persian Empire.
- c. 632 CE: Rise of Islam in the Arabian Peninsula.
- c. 1258 CE: Establishment of the Mongol Empire by Genghis Khan.
- c. 1517 CE: Ottoman Empire conquers Egypt and establishes its dominance over much of Southwest Asia.
- c. 1918 CE: Collapse of the Ottoman Empire after World War I.
Economic and Political Landscape of Southwest Asia
The economic and political landscape of Southwest Asia is complex and diverse, shaped by a confluence of factors including natural resources, geopolitical alliances, and historical legacies.
Key Industries, Map labeling southwest asia countries
The region is home to some of the world’s largest oil and gas reserves, making it a major player in the global energy market. Other key industries include agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing.
Trade Routes
Southwest Asia lies at the crossroads of several important trade routes, including the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz. These routes facilitate the flow of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Political Alliances
The region is characterized by a complex web of political alliances, often driven by shared economic interests or security concerns. Key alliances include the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
Major Economic Powers
The major economic powers in Southwest Asia include Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Qatar. These countries have used their oil wealth to develop diversified economies and become major players in the global financial system.
“The economic and political landscape of Southwest Asia is constantly evolving, driven by both internal and external factors. The region faces challenges such as political instability, economic inequality, and environmental degradation, but it also has the potential to be a major force in the global economy.”
– Prince Turki Al Faisal, former Saudi Arabian intelligence chief
Challenges and Opportunities in Southwest Asia: Map Labeling Southwest Asia Countries
Southwest Asia faces numerous challenges and opportunities that shape its present and future. Understanding these factors is crucial for addressing the region’s development and stability.
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is a critical challenge in Southwest Asia, where many countries are arid or semi-arid. The region’s population growth, urbanization, and climate change exacerbate water shortages. Initiatives such as desalination plants, water conservation programs, and regional cooperation are being implemented to address this issue.
Political Instability
Political instability has plagued Southwest Asia for decades. Conflicts, authoritarian regimes, and sectarian tensions have hindered economic development and social progress. International organizations, regional alliances, and diplomatic efforts play a role in promoting stability and conflict resolution.
Economic Diversification
Many Southwest Asian economies rely heavily on oil and gas exports, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy markets. Economic diversification is essential for sustainable growth and job creation. Governments are promoting sectors such as tourism, manufacturing, and technology to reduce dependence on hydrocarbons.
| Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| Water Scarcity | Desalination, water conservation, regional cooperation |
| Political Instability | Conflict resolution, international cooperation, regional alliances |
| Economic Diversification | Tourism, manufacturing, technology |
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of map labeling in understanding Southwest Asia?
Map labeling provides a visual representation of the region’s political and geographic boundaries, facilitating a deeper comprehension of its geopolitical dynamics.
How does the labeling of geographic features contribute to our understanding of Southwest Asia?
Labeling geographic features, such as mountain ranges, rivers, and bodies of water, provides insights into the region’s physical characteristics and their impact on human settlement and economic development.
What are the key historical events that have shaped the map of Southwest Asia?
The rise and fall of ancient empires, the spread of Islam, and the colonial era have all played significant roles in shaping the political boundaries of Southwest Asia.
