The equipment depreciates $400 per month. This statement holds significant implications for businesses, as depreciation plays a crucial role in determining the value of equipment over time, influencing tax liabilities, and shaping financial strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of depreciation, exploring its impact on equipment value, examining the factors that influence depreciation rates, and discussing the various methods used to account for depreciation.
Depreciation is an accounting practice that allocates the cost of an asset over its useful life. By recognizing the gradual decline in value of equipment due to wear and tear, obsolescence, and other factors, depreciation provides a systematic way to reduce the asset’s book value and reflect its diminishing worth.
Impact of Depreciation on Equipment Value

Depreciation is an accounting method that allocates the cost of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the asset’s value on the balance sheet and is used to recognize the gradual decline in an asset’s value due to usage, wear and tear, and obsolescence.
In the case of equipment that depreciates at a rate of $400 per month, the value of the equipment will decrease by $400 each month. This reduction in value is reflected in the company’s financial statements and affects the company’s taxable income.
For example, if a company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000 and it depreciates at a rate of $400 per month, the equipment’s value will be $9,600 after one month, $9,200 after two months, and so on.
Factors Influencing Depreciation Rate
The depreciation rate of an asset is influenced by several factors, including:
- Usage patterns:Equipment that is used heavily will depreciate more quickly than equipment that is used infrequently.
- Maintenance schedule:Equipment that is properly maintained will depreciate more slowly than equipment that is not maintained.
- Technological advancements:Equipment that is technologically advanced will depreciate more quickly than equipment that is not.
Methods of Depreciation
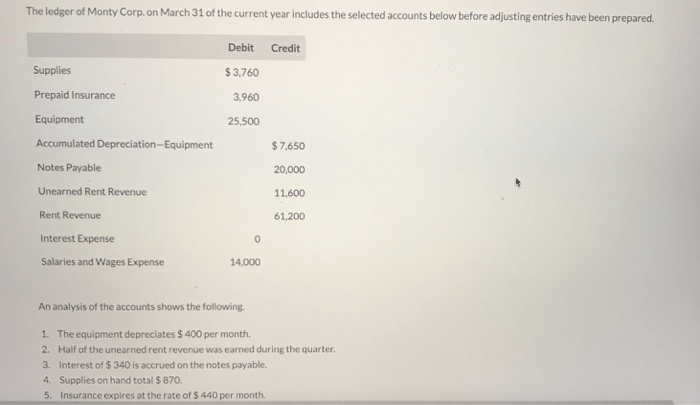
There are several methods of depreciation that can be used to account for the decline in equipment value. The most common methods are:
- Straight-line depreciation:This method allocates the cost of an asset evenly over its useful life.
- Declining-balance depreciation:This method allocates a larger portion of the cost of an asset to the early years of its useful life.
- Units-of-production depreciation:This method allocates the cost of an asset based on the number of units produced by the asset.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The straight-line method is the simplest to use, but it may not accurately reflect the actual decline in value of an asset. The declining-balance method allocates a larger portion of the cost of an asset to the early years of its useful life, which may be more accurate for assets that experience a rapid decline in value.
The units-of-production method allocates the cost of an asset based on the number of units produced by the asset, which may be more accurate for assets that are used heavily.
Tax Implications of Depreciation
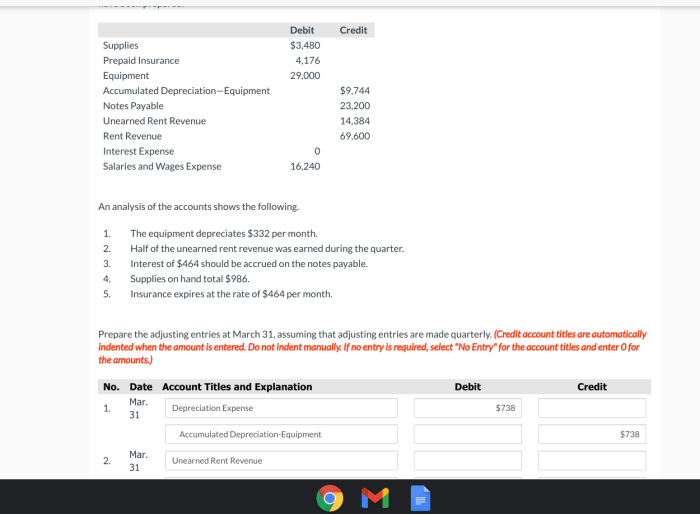
Depreciation has several tax implications for businesses. Depreciation deductions can reduce taxable income and potentially save on taxes. The amount of the depreciation deduction is determined by the method of depreciation used and the useful life of the asset.
For example, if a company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000 and it depreciates at a rate of $400 per month, the company can deduct $400 per month from its taxable income. This will reduce the company’s taxable income by $4,800 over the ten-year useful life of the asset.
Strategies for Managing Depreciation
Businesses can implement several strategies to manage depreciation effectively. These strategies include:
- Choosing the right depreciation method:The choice of depreciation method can have a significant impact on the company’s taxable income and cash flow.
- Optimizing the useful life of assets:Businesses can extend the useful life of assets by properly maintaining them and upgrading them when necessary.
- Selling assets before the end of their useful life:Businesses can sell assets before the end of their useful life to avoid taking a loss on the sale.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can manage depreciation effectively and maximize the financial benefits of depreciation.
Case Study: Depreciation of Equipment
A company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000. The equipment has a useful life of ten years and is depreciated at a rate of $400 per month using the straight-line method.
The following table shows the impact of depreciation on the equipment’s value and the company’s financial statements:
| Year | Beginning Value | Depreciation Expense | Ending Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $10,000 | $400 | $9,600 |
| 2 | $9,600 | $400 | $9,200 |
| 3 | $9,200 | $400 | $8,800 |
| 4 | $8,800 | $400 | $8,400 |
| 5 | $8,400 | $400 | $8,000 |
| 6 | $8,000 | $400 | $7,600 |
| 7 | $7,600 | $400 | $7,200 |
| 8 | $7,200 | $400 | $6,800 |
| 9 | $6,800 | $400 | $6,400 |
| 10 | $6,400 | $400 | $6,000 |
As shown in the table, the equipment’s value decreases by $400 each month. This reduction in value is reflected in the company’s financial statements and affects the company’s taxable income.
Helpful Answers: The Equipment Depreciates 0 Per Month
What is the impact of depreciation on equipment value?
Depreciation reduces the book value of equipment over time, reflecting its diminishing worth due to wear and tear, obsolescence, and other factors.
What factors influence the depreciation rate of equipment?
Usage patterns, maintenance schedule, and technological advancements are among the key factors that can influence the depreciation rate of equipment.
What are the different methods of depreciation?
Common depreciation methods include straight-line depreciation, declining balance depreciation, and units-of-production depreciation.
What are the tax implications of depreciation?
Depreciation deductions can reduce taxable income, potentially saving businesses on taxes.
What strategies can businesses implement to manage depreciation effectively?
Businesses can implement strategies such as optimizing depreciation schedules, considering salvage value, and planning for equipment replacement to effectively manage depreciation.
