Hesi case study congenital heart disease – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of congenital heart disease (CHD) through the lens of a captivating HESI case study. This in-depth analysis delves into the intricacies of CHD, its prevalence, impact, and the multifaceted approaches to its management, promising a profound understanding of this prevalent pediatric condition.
The HESI case study provides a compelling narrative, showcasing the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and diagnostic journey. This real-world account illuminates the challenges faced by individuals with CHD, highlighting the significance of early detection and intervention.
Definition and Overview
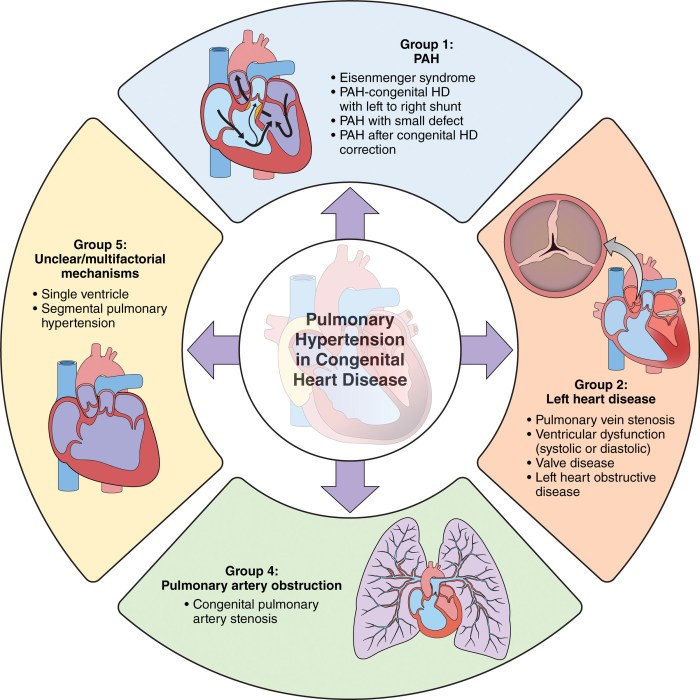
Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a group of structural abnormalities of the heart and major blood vessels present at birth. These abnormalities can range from mild to severe and can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
CHD is one of the most common birth defects, affecting approximately 8 out of every 1,000 live births. It is a leading cause of infant mortality and can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of children throughout their lives.
Types of CHD, Hesi case study congenital heart disease
There are many different types of CHD, each with its own unique set of symptoms and treatment options. Some of the most common types of CHD include:
- Atrial septal defect (ASD): A hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of the heart (atria).
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD): A hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).
- Tetralogy of Fallot: A combination of four heart defects that includes a VSD, pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Transposition of the great arteries: A condition in which the two main arteries that carry blood away from the heart are reversed.
HESI Case Study on CHD
The HESI case study on CHD presents the case of a 6-week-old infant with cyanosis, tachypnea, and poor feeding. The infant is diagnosed with tetralogy of Fallot and undergoes surgical repair at 6 months of age.
The case study highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of CHD. It also demonstrates the role of nurses in providing care and support to patients with CHD and their families.
Assessment and Management: Hesi Case Study Congenital Heart Disease

The diagnosis of CHD is based on a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. Echocardiography is the most commonly used imaging test for diagnosing CHD. It uses sound waves to create images of the heart and blood vessels.
The treatment of CHD depends on the type and severity of the defect. Some CHDs can be treated with medication, while others require surgery. Surgical repair is often the best option for severe CHDs.
Nursing Care
Nurses play a vital role in the care of patients with CHD. They provide preoperative and postoperative care, monitor patients for complications, and educate patients and families about CHD.
Nursing interventions for patients with CHD include:
- Monitoring vital signs and oxygen saturation
- Administering medications
- Providing wound care
- Educating patients and families about CHD
Patient and Family Education
Patient and family education is an essential part of the management of CHD. Nurses can provide education about CHD, its symptoms, treatment options, and long-term care.
Educational materials and resources for families of children with CHD include:
- The American Heart Association
- The Children’s Heart Foundation
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Ethical Considerations
The diagnosis and treatment of CHD raise a number of ethical considerations. These include:
- The right to informed consent
- The best interests of the child
- The allocation of scarce resources
It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of these ethical considerations and to make decisions that are in the best interests of the patient.
Future Directions in CHD Management
Research is ongoing to improve the diagnosis and treatment of CHD. Some of the current areas of research include:
- Developing new surgical techniques
- Improving the long-term outcomes of patients with CHD
- Preventing CHD
These research efforts are expected to lead to significant improvements in the care of patients with CHD in the future.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the prevalence of congenital heart disease?
CHD affects approximately 8 out of every 1,000 live births, making it one of the most common birth defects.
What are the common symptoms of CHD?
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of CHD, but may include shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and bluish skin (cyanosis).
How is CHD diagnosed?
CHD can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart), and other imaging tests.