The Organic Chemistry Reagents Cheat Sheet is an indispensable tool for students, researchers, and practitioners in the field of organic chemistry. It provides a comprehensive overview of the most important functional groups, reagents, and reaction mechanisms, empowering users to navigate the complexities of organic synthesis with ease.
This cheat sheet serves as a concise and accessible reference, guiding users through the fundamental principles of organic chemistry and equipping them with the knowledge necessary to design and execute successful synthetic strategies.
Introduction
An organic chemistry reagents cheat sheet is an invaluable tool that provides a concise and comprehensive overview of the most commonly used reagents in organic synthesis. It serves as a quick reference for researchers, students, and practitioners, enabling them to identify and select the appropriate reagents for their specific reactions.
Reagents in organic chemistry are substances that are used to bring about chemical transformations. They can be classified based on their functional group compatibility, which determines the types of reactions they can facilitate. A cheat sheet typically includes information on the name, structure, reactivity, and common reactions associated with each reagent.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties. The most important functional groups in organic chemistry include:
- Alkanes
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
- Alcohols
- Aldehydes
- Ketones
- Carboxylic acids
- Esters
- Amides
- Amines
Each functional group has its own characteristic reactivity and common reactions. For example, alkenes are known for their ability to undergo addition reactions, while alcohols can be oxidized to form aldehydes or ketones.
Reagents
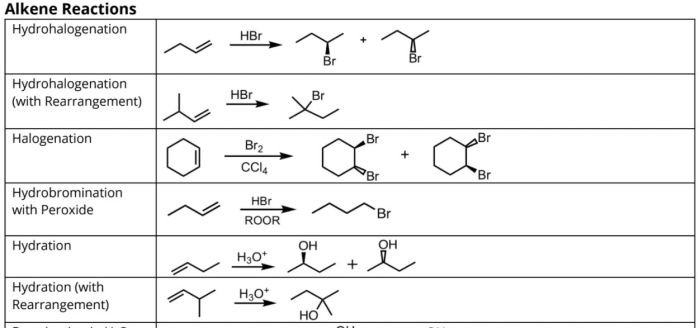
Reagents can be organized based on their functional group compatibility. For example, reagents that are specific for alkenes include:
- Potassium permanganate (KMnO 4)
- Bromine (Br 2)
- Hydrogen bromide (HBr)
The following table provides a more comprehensive list of reagents, their structures, reactivity, and examples of reactions:
| Reagent | Structure | Reactivity | Examples of Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) | KMnO4 | Oxidizing agent | Oxidation of alkenes to diols |
| Bromine (Br2) | Br2 | Electrophile | Addition of bromine to alkenes |
| Hydrogen bromide (HBr) | HBr | Electrophile | Addition of hydrogen bromide to alkenes |
Reaction Mechanisms
Reaction mechanisms are step-by-step descriptions of how chemical reactions occur. They involve the breaking and formation of chemical bonds, and the movement of electrons. Understanding reaction mechanisms is essential for predicting the outcome of reactions and designing new synthetic methods.
The basic principles of organic reaction mechanisms include:
- Nucleophilic attack
- Electrophilic attack
- Free radical reactions
- Pericyclic reactions
Reagents play a crucial role in reaction mechanisms. They can act as nucleophiles, electrophiles, or catalysts. For example, potassium permanganate (KMnO 4) is a strong oxidizing agent that can oxidize alkenes to diols. This reaction proceeds through a nucleophilic attack by the permanganate ion on the alkene.
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions are the specific parameters under which a reaction is carried out. They include temperature, solvent, concentration, and pressure. Reaction conditions can influence the outcome of a reaction by affecting the rate, selectivity, and yield of the desired product.
For example, the reaction of an alkene with hydrogen bromide (HBr) to form an alkyl bromide can be carried out under different conditions to give different products. If the reaction is carried out in a polar solvent at low temperature, the major product will be the Markovnikov product.
However, if the reaction is carried out in a nonpolar solvent at high temperature, the major product will be the anti-Markovnikov product.
Examples and Applications
Organic chemistry reagents are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Synthesis of new compounds
- Analysis of organic compounds
- Drug discovery
- Materials science
- Environmental chemistry
For example, the reagent potassium permanganate (KMnO 4) is used in the synthesis of a variety of compounds, including diols, aldehydes, and ketones. It is also used in the analysis of organic compounds, such as the detection of unsaturation. In drug discovery, reagents are used to synthesize new compounds that may have potential therapeutic applications.
In materials science, reagents are used to create new materials with desired properties. In environmental chemistry, reagents are used to analyze and remediate environmental pollutants.
Common Queries: Organic Chemistry Reagents Cheat Sheet
What are the benefits of using an organic chemistry reagents cheat sheet?
An organic chemistry reagents cheat sheet provides quick and easy access to essential information, saving time and effort during research and synthesis.
What types of reagents are included in the cheat sheet?
The cheat sheet includes a wide range of reagents, organized by their functional group compatibility, making it easy to find the right reagent for a specific reaction.
How can I use the cheat sheet to understand reaction mechanisms?
The cheat sheet provides a step-by-step breakdown of key reaction mechanisms, highlighting the role of reagents in each step.