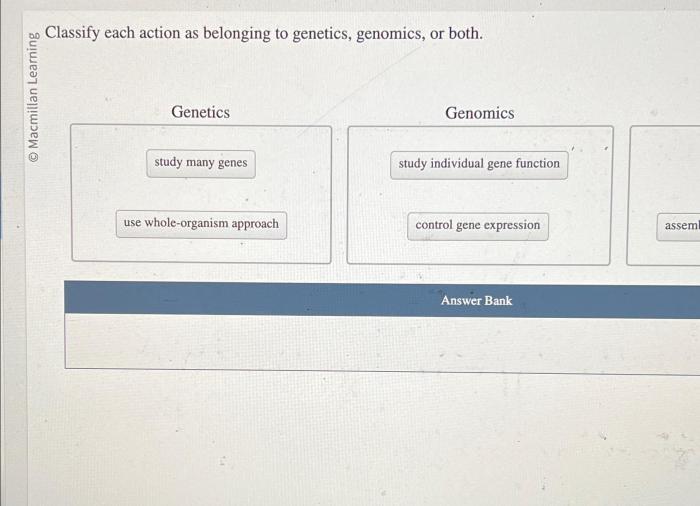
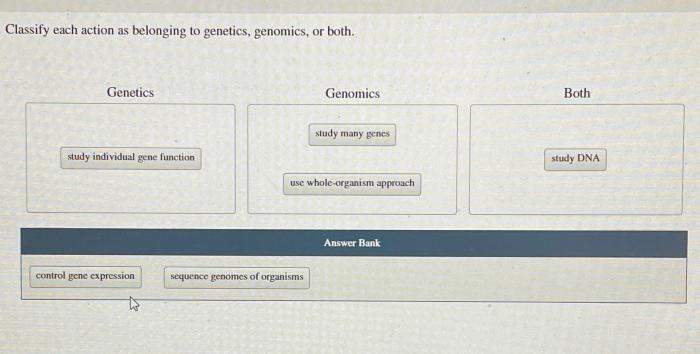
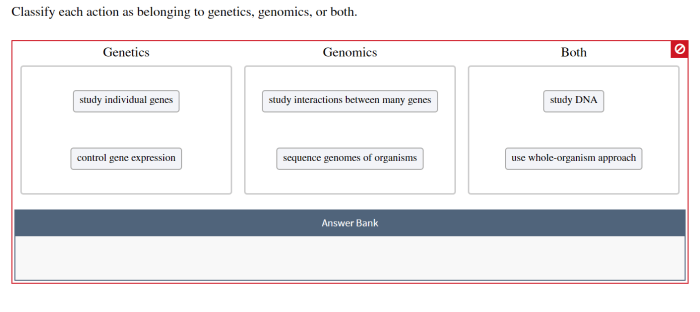
Classify each action as belonging to genetics genomics or both – Classify each action as belonging to genetics, genomics, or both, an in-depth exploration of the fields of genetics and genomics, delving into their definitions, techniques, applications, ethical implications, and future directions. This comprehensive guide provides a clear understanding of the distinctions and interconnections between these disciplines, empowering readers with the knowledge to navigate the rapidly evolving landscape of genetic and genomic research.
Genetics focuses on the study of individual genes and their inheritance patterns, while genomics examines the entire genome, including the interactions between genes and their environment. By unraveling the complexities of our genetic makeup, these fields have revolutionized our understanding of biology and hold immense promise for advancing personalized medicine, unlocking new treatments, and shaping the future of healthcare.
Definition and Scope: Classify Each Action As Belonging To Genetics Genomics Or Both
Genetics is the study of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. It seeks to understand how traits are passed from one generation to the next and how genetic factors contribute to phenotypic variation.
Genomics is a broader field that encompasses genetics and the study of the entire genome, including its structure, function, and evolution. It involves the sequencing, analysis, and interpretation of large-scale genetic data.
Key Differences:
- Genetics focuses on individual genes and their inheritance patterns, while genomics examines the entire genome.
- Genetics primarily uses Mendelian principles and classical genetic techniques, while genomics employs high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics tools.
Techniques and Methodologies
Genetics:
- Pedigree analysis to trace inheritance patterns.
- Genetic mapping to identify the location of genes.
- DNA sequencing to determine the genetic code.
Genomics:
- Whole-genome sequencing to obtain a complete genetic profile.
- Comparative genomics to identify similarities and differences between genomes.
- Functional genomics to study gene expression and regulation.
Advancements:
- Improved understanding of genetic diseases.
- Development of personalized medicine approaches.
- Identification of genetic markers for complex traits.
Applications in Medicine and Healthcare
Personalized Medicine:
- Genetic testing to identify individuals at risk for certain diseases.
- Tailored treatment plans based on genetic profiles.
- Development of targeted therapies for genetic disorders.
New Treatments and Therapies:
- Gene therapy to correct genetic defects.
- Genome editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 for precision gene manipulation.
- Identification of genetic targets for drug development.
Ethical and Social Implications, Classify each action as belonging to genetics genomics or both
Ethical Considerations:
- Informed consent and privacy concerns.
- Potential for genetic discrimination.
- Balancing individual rights with societal responsibilities.
Social and Economic Impact:
- Access to genetic testing and its cost implications.
- Potential for genetic enhancement and designer babies.
- Impact on insurance and employment practices.
Future Directions
Emerging Trends:
- Single-cell genomics to study cellular heterogeneity.
- Epigenetics to understand the role of environmental factors in gene expression.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning for data analysis and interpretation.
Potential Impact:
- Precision medicine and personalized therapies.
- Improved understanding of disease mechanisms.
- New approaches to genetic counseling and risk assessment.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between genetics and genomics?
Genetics focuses on the study of individual genes and their inheritance patterns, while genomics examines the entire genome, including the interactions between genes and their environment.
How are genetics and genomics used in medicine?
Genetics and genomics are used in medicine to identify individuals at risk for certain diseases, develop new treatments and therapies, and provide personalized medicine approaches tailored to individual genetic profiles.
What are the ethical implications of genetic and genomic research?
The ethical implications of genetic and genomic research include issues related to privacy, discrimination, and the potential misuse of genetic information.