Which mineral strengthens and repairs tooth enamel – Delving into the realm of dental health, we embark on a quest to uncover the enigmatic mineral that empowers our teeth with resilience and restorative prowess. This mineral, the guardian of our pearly whites, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of our smiles.
As we unravel its secrets, we will delve into the fascinating world of tooth enamel and its remarkable ability to heal and protect.
Tooth enamel, the outermost layer of our teeth, serves as a formidable barrier against the relentless onslaught of decay. Composed primarily of hydroxyapatite crystals, this intricate latticework provides unparalleled strength and durability. However, despite its resilience, tooth enamel is not impervious to the ravages of time and environmental factors.
Fortunately, nature has bestowed upon us a remarkable mineral that possesses the remarkable ability to strengthen and repair this vital tissue.
1. Introduction to Tooth Enamel and its Importance
Tooth enamel is the hard, outermost layer of the tooth that protects it from decay. It is composed primarily of hydroxyapatite, a mineral that contains calcium and phosphate ions. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and is essential for protecting teeth from damage caused by acids, bacteria, and wear and tear.
2. Role of Minerals in Strengthening Tooth Enamel
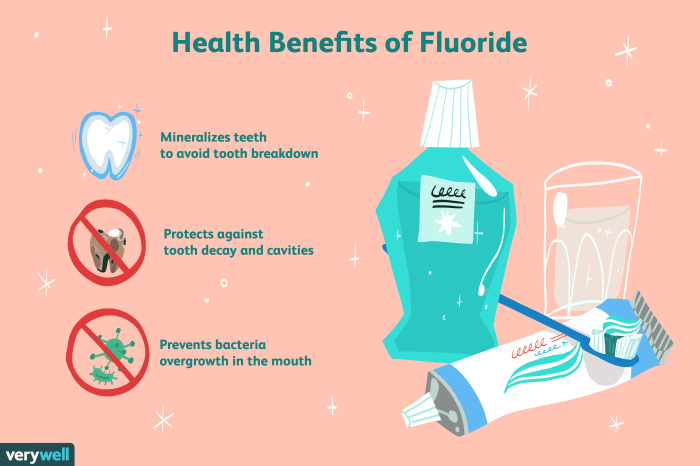
Tooth remineralization is the process by which minerals are deposited back into the tooth enamel, strengthening it and repairing damage. The following minerals are essential for tooth remineralization:
- Calcium
- Phosphate
- Fluoride
- Magnesium
- Potassium
These minerals interact with tooth enamel to form a strong, protective layer that helps to prevent decay.
3. The Role of Fluoride in Tooth Enamel Repair
Fluoride is a mineral that has been shown to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent decay. Fluoride works by replacing hydroxyl ions in the hydroxyapatite crystals of tooth enamel with fluoride ions, creating a more acid-resistant surface. Fluoride can be found in a variety of sources, including drinking water, toothpaste, and mouthwash.
The use of fluoride-containing products has been shown to reduce the risk of tooth decay by up to 40%. Fluoride can also help to reverse the early stages of tooth decay, remineralizing the enamel and preventing further damage.
4. Other Minerals and their Contribution to Tooth Enamel Health
In addition to fluoride, a number of other minerals contribute to tooth enamel health, including:
- Calcium: Calcium is the most abundant mineral in tooth enamel. It helps to strengthen the enamel and make it more resistant to decay.
- Phosphate: Phosphate is the second most abundant mineral in tooth enamel. It helps to form the hydroxyapatite crystals that make up the enamel.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is a trace mineral that helps to stabilize the hydroxyapatite crystals in tooth enamel.
- Potassium: Potassium is a trace mineral that helps to maintain the pH balance of the oral environment.
The availability of these minerals in the diet and through oral hygiene practices is essential for maintaining healthy tooth enamel.
5. Clinical Applications and Preventive Measures
There are a number of dental procedures that utilize minerals to strengthen tooth enamel, including:
- Fluoride treatments: Fluoride treatments can be applied to the teeth in the form of gels, varnishes, or mouthwashes. These treatments help to strengthen the enamel and prevent decay.
- Dental sealants: Dental sealants are thin, plastic coatings that are applied to the chewing surfaces of the teeth. Sealants help to protect the teeth from decay by sealing out bacteria and acids.
In addition to these clinical procedures, there are a number of preventive measures that can be taken to protect tooth enamel, including:
- Regular brushing and flossing: Brushing and flossing helps to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth, which can help to prevent decay.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is rich in calcium, phosphate, and other essential minerals can help to maintain healthy tooth enamel.
- Avoiding sugary foods and drinks: Sugary foods and drinks can damage tooth enamel and increase the risk of decay.
By following these preventive measures, you can help to protect your tooth enamel and maintain a healthy smile.
Commonly Asked Questions: Which Mineral Strengthens And Repairs Tooth Enamel
What is the primary function of tooth enamel?
Tooth enamel serves as the protective shield of our teeth, safeguarding them from decay and external threats.
How does fluoride contribute to tooth enamel health?
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel by penetrating its crystalline structure and promoting remineralization, a process that replenishes lost minerals and restores the enamel’s integrity.
What are some dietary sources of fluoride?
Fluoride can be obtained from various sources, including fluoridated water, toothpaste, and certain foods such as fish and tea.